Matplotlib
The next two lines are the same:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
They help us import the matplotlib plotting library. Next we can do some 2D plotting, using the PyTorch tensor:
import torch
img = torch.empty(8,8,3).uniform_(0, 1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
plt.close()
This will plot what is called 2d plot RGB image.

If we need just to draw a single line we will use something like this:
N = 20
t = torch.randn(N)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# monkey patching `torch.Tensor`
torch.Tensor.ndim = property(lambda x: len(x.size()))
plt.plot(t)
plt.show()
plt.close()
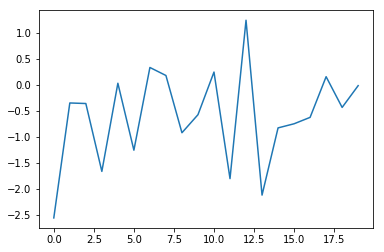
We can now use the PyTorch lerp function to draw:
steps = 100
N = 2
first = torch.zeros(N)
save = torch.zeros(steps, N) # for plot
for _ in range (0,steps):
save[_, 0] = first[0].item()
save[_, 1] = first[1].item()
second = torch.rand(N)
first = first.lerp_(second, 0.1)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.Tensor.ndim = property(lambda x: len(x.size()))
plt.plot(save[:,0])
plt.plot(save[:,1])
plt.show()
plt.close()
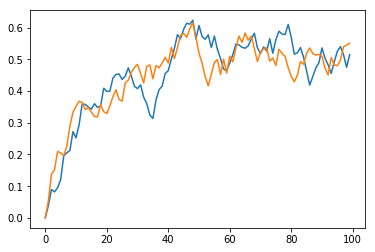
This one is another attempt with lerp that draws doodles:
steps = 100
N = 2
start = torch.zeros(N)
lerp = []
lerp2 = []
for _ in range (0,steps):
lerp.append(start[0].item())
lerp2.append(start[1].item())
end = torch.rand(N)
start = start.lerp_(end, 0.1)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(lerp, lerp2)
plt.plot(lerp2, lerp)
plt.show()
plt.close()
