Creating Github Pull Requests
- Create a Pull Request
- You just need to click a button Fork.
- Clone the repo where you were redirected
- Setup the fork to track upstream
- Make it even
- Create a branch and add your updates
- Push your updates to origin
- Creating a Pull request
Create a Pull Request
Let’s create a fork of the PyTorch project first, but this procedure is the same for any other project.
You just need to click a button Fork.
and you will be redirected to github.com/USERNAME/pytorch.
Once redirected:
Clone the repo where you were redirected
git clone https://github.com/dejanbatanjac/pytorch.git pytorch-fork
cd pytorch-fork
Setup the fork to track upstream
Click the [Clone or download] button

You will have HTTPS or SSH options:
git remote add upstream https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch.git
# or ...
git remote add upstream git@github.com:USERNAME/pytorch.git
Now if you issue a command git config -l you should have remote.upstream.url set.
You can check the same with git remote -v that will return at this point:
pytorch-fork>git remote -v
origin https://github.com/USERNAME/pytorch.git (fetch)
origin https://github.com/USERNAME/pytorch.git (push)
upstream https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch.git (fetch)
upstream https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch.git (push)
After day or two you will notice, your fork will be behind the master.
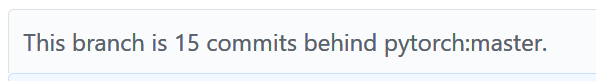
So what to do?
Make it even
cd pytorch-fork
git checkout master
git fetch upstream
git checkout master
git merge --no-edit upstream/master
git push
Then you will get this message:
This branch is even with pytorch:master.
Create a branch and add your updates
git checkout -b new-branch
git push --set-upstream origin new-branch
Push your updates to origin
git commit
git push
Creating a Pull request